

|
|
|


|
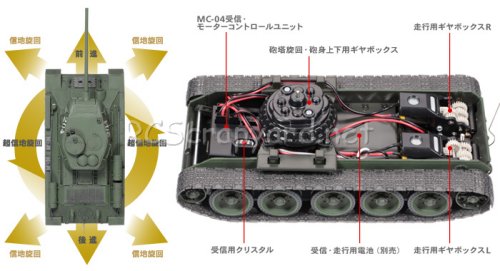
Tamiya Russian Medium Tank T-34-85 - 48208 (Radio Controlled Model Review)1/35 Scale Electric Tank -
Released by Tamiya on April 25, 2009, the 1/35 R/C Russian Medium Tank T-34-85 (#48208) came with a 4-channel radio system.
▼ Scroll Down for More Images ▼
Rating: 4
|








|
|
|

|



|
Hints, Tips and Information
How to avoid Radio Interference
1/ The first consideration when installing your Receiver into your Electrically Powered Model is to make sure it is well away from the Negative Battery terminal, and the Motor. The Magnetic field can cause stuttering type interference at times of high current draw (i.e., Fast Acceleration) |









|






|
|
|
|
Hints, Tips and Information Electric Motors for RC ModelsWinds and Turns
Q/ What does 15x2 or 17x3 mean? |
Information and AdviceElectronic Speed ControllersHistory
ESC were originally developed to be used in conjunction with brushed 27T stock and modified motors in the late 1970s, early 1980s. Compared to modern day Controllers, they were Bulky and heavy, constructed using basic resistors, rheostats, capacitors and transistors, crammed together on a simple circuit board, to provide stepped but smooth acceleration when compared to the old mechanical, servo operated sweeper Speed Controllers. An Electronic Switch to change the direction of current flow was used on some of these early ESC to give reverse operation. Although they were a vast improvement on the old mechanical speedos of the time, they were expensive, jerky to control, and prone to burn out if not carefully looked after. |
|
RC Models:
|
Radio & Motors: |
Other
Accessories: |